
University of Leeds awards honorary degrees
Olympic boxer, Nicola Adams, and Sir Peter Hendy, Leeds graduate and the new Chairman of Network Rail, are amongst a host of distinguished individuals receiving an honorary degree this year

Olympic boxer, Nicola Adams, and Sir Peter Hendy, Leeds graduate and the new Chairman of Network Rail, are amongst a host of distinguished individuals receiving an honorary degree this year

University of Leeds researchers are playing a key role in a €7 million international collaboration, granted by the European Union's Horizon 2020 fund, to develop new, eco-friendly pesticides.
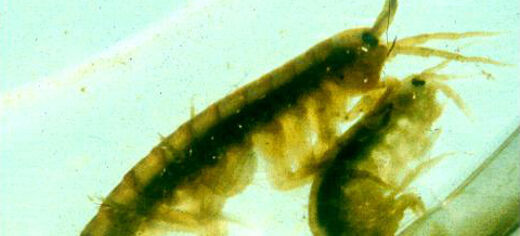
Parasites can play an important role in driving cannibalism, according to a new research which looked at cannibalism among freshwater shrimp in Northern Ireland.

New research into an Icelandic eruption has shed light on how the Earth's crust forms, according to a paper published today in Nature.

A collaboration between Leeds-based The Phoenix Partnership (TPP) and the University of Leeds has won a national Research Council UK impact award from Innovate UK, the UK's innovation agency.

Research by students at the University of Leeds has uncovered the extraordinary story of a First World War officer who ended up marrying the nurse who condemned him as a German spy.
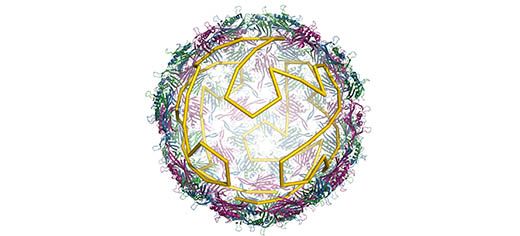
A new study has solved a long-standing puzzle of how common viruses reproduce themselves during an infection, opening up new possibilities for treating a range of diseases from HIV to the common cold.

Exploring the impact of innovation in technology during the Great War and shedding light on how people resisted the war are just two of many insights offered by new University of Leeds research.
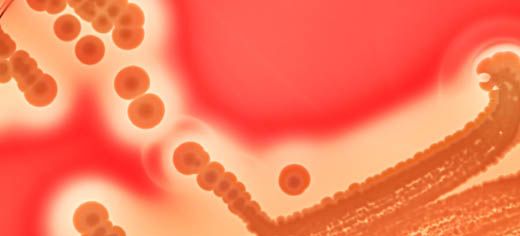
Researchers have identified a resistance protein that allows bacteria to survive chlorhexidine, an antiseptic commonly used in wipes, cleansers and mouthwashes in hospitals.
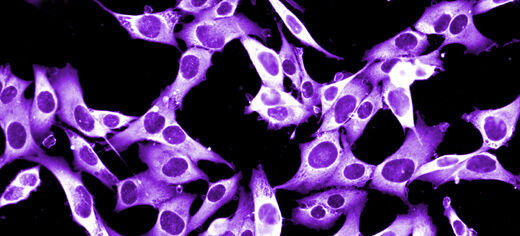
Scientists at Leeds have found that the immune system's behaviour can act as an early warning alarm that detects cancer recurrence, and this could offer a chance for pre-emptive treatment.